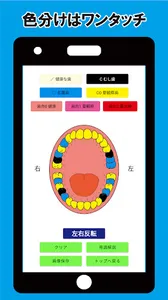
Let's use the dental examination sketch app! !!
Usage is simple. Color-code your mouth based on the symbols of the dental examination results (treatment recommendation) received from school dental examinations, adult dental examinations, pregnant women's dental examinations, etc.
By doing so, you will be able to remind yourself of your mouth.
(How to use)
(1) Select the symbol button.
(2) Tap the corresponding part to paint the color.
▼ The same color can be applied to other parts by continuous tapping.
▼ You can delete the color by tapping the same part twice.
▼ The color does not reach the parts that are not applicable.
(3) You can save the image.
(4) Glossary of dental examination symbols is also included.
(5) You can check the result of the medical examination while you are in the mirror in the "reverse mode".
★ "5 is 〇, 4 diagonal lines. 3 is C, 2 Shio" This is!
Maybe everyone once wondered, "What is that?"
Actually, I am one of them, and I don't know what I was saying at that time, but I wish the results of the medical examination were good! I was only thinking.
However, if you know the jargon, you will be able to know the condition of your mouth even more.
I understand that you need to be careful in the future, so this time I will tell you about the "symbols used in school dental examinations".
★
▼ Diagonal line (/): Healthy tooth / Current tooth
Currently growing milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Healthy teeth. A tooth that is not cavities and has never been treated.
▼ CIO (CO): Teeth required for observation
Teeth that are not obvious cavities but require follow-up.
Teeth that may become cavities if left as they are if there is a problem with lifestyle, such as coloring, cloudiness or white spots (white without gloss like chalk).
It is important to follow up to prevent tooth decay by the person, school, dentist, etc.
How to brush your teeth and review your lifestyle will be the keys to the future.
▼ C (C): Caries / Caries
It's a tooth decay. Even if treatment is recommended, if the patient has not been examined, it is also referred to as an untreated tooth in the sense that it is an untreated tooth.
After treatment, it is called secondary caries to have cavities again.
In the past, it was divided into C1 (Shiichi), C2 (Sini), and C3 (Shisan) according to the progress of tooth decay, but now that classification has been abolished.
▼ Shiyon (C4): Residual root teeth
Teeth with only roots. In the worst case, it may result in tooth extraction.
The classification of C1, C2 and C3 has disappeared, but this C4 is distinguished from C.
▼ Maru (〇): Treated tooth
A tooth that has been treated for caries.
Even if you treat it with great care, you may get cavities again.
▼ Sankaku (△): Lost tooth
Lost teeth. Including cases where there are no teeth by nature.
For the sake of orthodontic treatment, it may be expressed as "▲" when the tooth is extracted for convenience.
▼ X (X): Milk teeth that need attention
Milk teeth that need to be carefully decided whether to leave
= It is a milk tooth that should be pulled out soon.
It is mainly diagnosed when permanent teeth grow.
The condition is permanent teeth, deciduous teeth that are likely to affect, or if permanent teeth have already grown from below.
In many cases, X-rays are taken to make the final decision as to whether or not the tooth should be extracted.
▼ Shi: Sealant
Teeth that have been treated prophylactically. Treat as a healthy tooth.
Treatment to prevent tooth decay by pouring medicine into the groove of the tooth.
▼ Sa: Sahoride
Teeth coated with a drug to stop the progress of tooth decay.
Strictly speaking, it is called "Sea Marsa".
★
Check for inflammation in the so-called gum area, called the gums, that is, for gingival inflammation and periodontitis.
▼ Gingiva 0; No abnormality
No inflammation of the gums
▼ Gingiva 1: Observation required (Gio: GO)
Those who have mild inflammation of the gingiva but no tartar deposits and require regular observation.
The condition of the gums that eliminates inflammation by careful brushing.
There is a risk of leading to gingival inflammation and periodontitis in the future.
Therefore, you must make sure to remove the plaque between your teeth and gums.
Be sure to take care of areas where plaque tends to accumulate, such as gaps in your teeth, such as using dental floss as well as a toothbrush.
It is also important to build a body that is less prone to inflammation.
If you get stressed or sleep deprived, inflammation of the whole body is likely to occur, so it is good to keep in mind a lifestyle that does not cause it.
▼ Gingiva 2: Close examination required Person with periodontal disease (G: G)
Persons with periodontal disease that require diagnosis by a dentist.
Persons with or suspected periodontitis
Those who have tartar and have inflammatory symptoms (redness, swelling, bleeding, etc.) in the gums.
Persons suspected of having gingival overgrowth (gingival overgrowth) ... Gingival muffled condition
▼ ZS (ZS): Tartar
A state in which dirt (plaque) on the teeth has solidified into stones.
This condition cannot be removed with a toothbrush and requires specialized treatment.
★
Temporomandibular joints, dentition, occlusion, plaque, periodontal pockets, tooth mobility, etc. may be examined.
Finally, I will summarize it with a brief summary.
Teeth condition
/ (Healthy teeth) Healthy teeth. Not a tooth decay and a tooth that has never been treated
C (cavity) tooth melted by acid
〇 (Treatment tooth) A tooth that has been treated for dental caries
CO (Observation required tooth) A tooth that is not obvious caries but requires follow-up
△ (lost tooth) A missing tooth. Including cases where there are no teeth by nature
× (Be careful milk teeth) Milk teeth that need to be carefully considered not to be pulled out
Teeth that have undergone preventive measures. Treat as a healthy tooth
Sa (Sahoride) Teeth coated with a drug to stop the progression of tooth decay
Usage is simple. Color-code your mouth based on the symbols of the dental examination results (treatment recommendation) received from school dental examinations, adult dental examinations, pregnant women's dental examinations, etc.
By doing so, you will be able to remind yourself of your mouth.
(How to use)
(1) Select the symbol button.
(2) Tap the corresponding part to paint the color.
▼ The same color can be applied to other parts by continuous tapping.
▼ You can delete the color by tapping the same part twice.
▼ The color does not reach the parts that are not applicable.
(3) You can save the image.
(4) Glossary of dental examination symbols is also included.
(5) You can check the result of the medical examination while you are in the mirror in the "reverse mode".
★ "5 is 〇, 4 diagonal lines. 3 is C, 2 Shio" This is!
Maybe everyone once wondered, "What is that?"
Actually, I am one of them, and I don't know what I was saying at that time, but I wish the results of the medical examination were good! I was only thinking.
However, if you know the jargon, you will be able to know the condition of your mouth even more.
I understand that you need to be careful in the future, so this time I will tell you about the "symbols used in school dental examinations".
★
▼ Diagonal line (/): Healthy tooth / Current tooth
Currently growing milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Healthy teeth. A tooth that is not cavities and has never been treated.
▼ CIO (CO): Teeth required for observation
Teeth that are not obvious cavities but require follow-up.
Teeth that may become cavities if left as they are if there is a problem with lifestyle, such as coloring, cloudiness or white spots (white without gloss like chalk).
It is important to follow up to prevent tooth decay by the person, school, dentist, etc.
How to brush your teeth and review your lifestyle will be the keys to the future.
▼ C (C): Caries / Caries
It's a tooth decay. Even if treatment is recommended, if the patient has not been examined, it is also referred to as an untreated tooth in the sense that it is an untreated tooth.
After treatment, it is called secondary caries to have cavities again.
In the past, it was divided into C1 (Shiichi), C2 (Sini), and C3 (Shisan) according to the progress of tooth decay, but now that classification has been abolished.
▼ Shiyon (C4): Residual root teeth
Teeth with only roots. In the worst case, it may result in tooth extraction.
The classification of C1, C2 and C3 has disappeared, but this C4 is distinguished from C.
▼ Maru (〇): Treated tooth
A tooth that has been treated for caries.
Even if you treat it with great care, you may get cavities again.
▼ Sankaku (△): Lost tooth
Lost teeth. Including cases where there are no teeth by nature.
For the sake of orthodontic treatment, it may be expressed as "▲" when the tooth is extracted for convenience.
▼ X (X): Milk teeth that need attention
Milk teeth that need to be carefully decided whether to leave
= It is a milk tooth that should be pulled out soon.
It is mainly diagnosed when permanent teeth grow.
The condition is permanent teeth, deciduous teeth that are likely to affect, or if permanent teeth have already grown from below.
In many cases, X-rays are taken to make the final decision as to whether or not the tooth should be extracted.
▼ Shi: Sealant
Teeth that have been treated prophylactically. Treat as a healthy tooth.
Treatment to prevent tooth decay by pouring medicine into the groove of the tooth.
▼ Sa: Sahoride
Teeth coated with a drug to stop the progress of tooth decay.
Strictly speaking, it is called "Sea Marsa".
★
Check for inflammation in the so-called gum area, called the gums, that is, for gingival inflammation and periodontitis.
▼ Gingiva 0; No abnormality
No inflammation of the gums
▼ Gingiva 1: Observation required (Gio: GO)
Those who have mild inflammation of the gingiva but no tartar deposits and require regular observation.
The condition of the gums that eliminates inflammation by careful brushing.
There is a risk of leading to gingival inflammation and periodontitis in the future.
Therefore, you must make sure to remove the plaque between your teeth and gums.
Be sure to take care of areas where plaque tends to accumulate, such as gaps in your teeth, such as using dental floss as well as a toothbrush.
It is also important to build a body that is less prone to inflammation.
If you get stressed or sleep deprived, inflammation of the whole body is likely to occur, so it is good to keep in mind a lifestyle that does not cause it.
▼ Gingiva 2: Close examination required Person with periodontal disease (G: G)
Persons with periodontal disease that require diagnosis by a dentist.
Persons with or suspected periodontitis
Those who have tartar and have inflammatory symptoms (redness, swelling, bleeding, etc.) in the gums.
Persons suspected of having gingival overgrowth (gingival overgrowth) ... Gingival muffled condition
▼ ZS (ZS): Tartar
A state in which dirt (plaque) on the teeth has solidified into stones.
This condition cannot be removed with a toothbrush and requires specialized treatment.
★
Temporomandibular joints, dentition, occlusion, plaque, periodontal pockets, tooth mobility, etc. may be examined.
Finally, I will summarize it with a brief summary.
Teeth condition
/ (Healthy teeth) Healthy teeth. Not a tooth decay and a tooth that has never been treated
C (cavity) tooth melted by acid
〇 (Treatment tooth) A tooth that has been treated for dental caries
CO (Observation required tooth) A tooth that is not obvious caries but requires follow-up
△ (lost tooth) A missing tooth. Including cases where there are no teeth by nature
× (Be careful milk teeth) Milk teeth that need to be carefully considered not to be pulled out
Teeth that have undergone preventive measures. Treat as a healthy tooth
Sa (Sahoride) Teeth coated with a drug to stop the progression of tooth decay
Show More