In this data collection app, users design surveys, trigger reminders, and upload geocoded data for analysis. Includes offline functionality, centralized server uploads, and educational resources on computational thinking.
About IDS UCLA
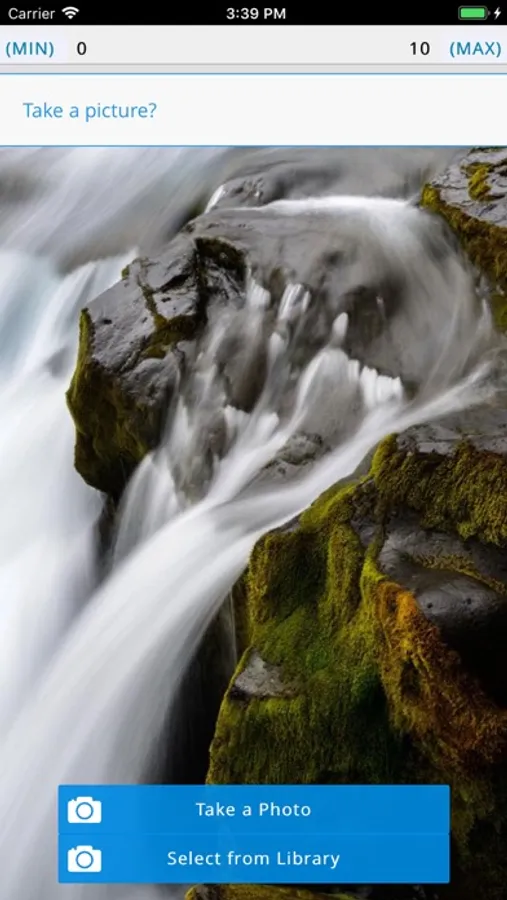
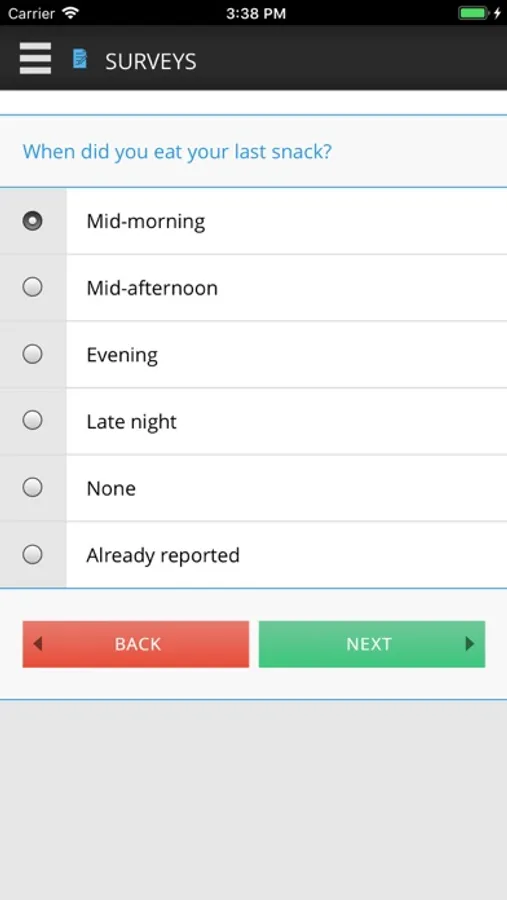
IDS UCLA is a data collection tool. It provides mobile-based data capture through inquiry-based surveys and temporally triggered reminders. All captured data are automatically timestamped, geocoded and uploaded to a centralized ohmage server for analysis and visualization. IDS UCLA is fully functional without network connectivity and can run on multiple mobile phone platforms.
Through IDS UCLA students use mobile phones and web services to systematically collect and interpret data about issues important to them and their communities. The goal of IDS UCLA is to strengthen STEM instruction throughout our educational system and to develop innovative methods for educating and engaging students in computational thinking and data analysis.
The core lessons in the ohmage units will be framed around principles of Computational Thinking. Specifically, through Participatory Sensing campaigns, students will identify phenomena to study, consider "designs" for how data are to be collected, and rally the computational resources to execute their plans. Along the way they will grapple with questions related to the nature of data (its representation, formats and protocols for sharing) and of algorithms (rules governing data collection, strategies for analysis). Students will learn about classical themes in Computer Science, from databases to networking, as well as lessons in Statistics, from visualization to basic inference.
Through IDS UCLA students use mobile phones and web services to systematically collect and interpret data about issues important to them and their communities. The goal of IDS UCLA is to strengthen STEM instruction throughout our educational system and to develop innovative methods for educating and engaging students in computational thinking and data analysis.
The core lessons in the ohmage units will be framed around principles of Computational Thinking. Specifically, through Participatory Sensing campaigns, students will identify phenomena to study, consider "designs" for how data are to be collected, and rally the computational resources to execute their plans. Along the way they will grapple with questions related to the nature of data (its representation, formats and protocols for sharing) and of algorithms (rules governing data collection, strategies for analysis). Students will learn about classical themes in Computer Science, from databases to networking, as well as lessons in Statistics, from visualization to basic inference.