About BlasToolsPro
BlasToolPro is a calculator/converter with more than 100 formulas to provide solutions for such topics as
1. Blast Pattern Design
1.1. Bench Height
1.2. Hole Diameter
1.3. Burden
1.4. Spacing
1.5. Sub-Drill Depth
1.6. Top Stemming
1.7. Deck Stemming
1.8. Base Charge Length
2. Delay Timing
2.1. Hole-to-Hole delays
2.2. Row-to-Row delays
2.3. Avoid supersonic face velocity
2.4. Estimating vibration frequency
2.5. Delay scatter
2.6. Out-of-sequence probability
2.7. Probability of close firing
3. Volume, Weight and Powder Factors
3.1. Volume of Rock per blast hole
3.2. Weight of Rock per blast-hole
3.3. Weight of Explosives per blast-hole
3.4. Loading Density
3.5. Powder Factor
4. Working with Angled Holes
4.1. Hole 'Look-out' distance
4.2. Required hole angle
4.3. Required hole length
4.4. Burden - two angled holes
4.5. Stemming - two angled holes
4.6. Collar distance - two angled holes
5. Pre-split Design
5.1. Pre-split spacing
5.2. Pre-split charge load
5.3. Pre-split stemming height
5.4. Pre-split hole diameter
5.5. Pre-split explosive diameter
6. Decoupled Charges
6.1. Coupling Ratio
6.2. Dropped explosive cartridge diameter
6.3. Decoupled Charge Effective Density
7. Wet Hole Formulas
7.1. No. of Cartridges to clear Water
7.2. Final Height of Water in Wet Hole
8. Abney Levels and Clinometers
8.1. Calculate Bench Height
8.2. Calculate Toe Burden
8.3. Face Angle
9. Scaled Distance and Blast Vibration
9.1. Actual Scaled Distance
9.2. Max Charge Weight
9.3. Minimum Distance
9.4. Predicting Vibration
9.5. Site specific k factor
9.6. Site specific b exponent
9.7. Distance from seismic data
9.8. Acceleration from PPV
9.9. Displacement from PPV
9.10. Explosive Quantity from PPV
9.11. K Factor Converting
9.12. Estimated p-wave velocity
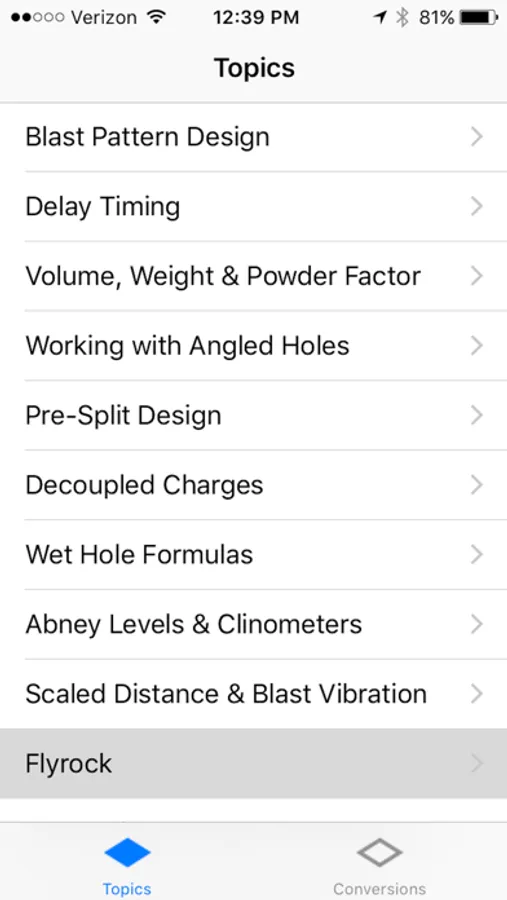
10. Flyrock
10.1. Average Muckpile Displacement
10.2. Extreme Flyrock
10.3. Burden Velocity and Throw
10.4. Burden Based on Throw
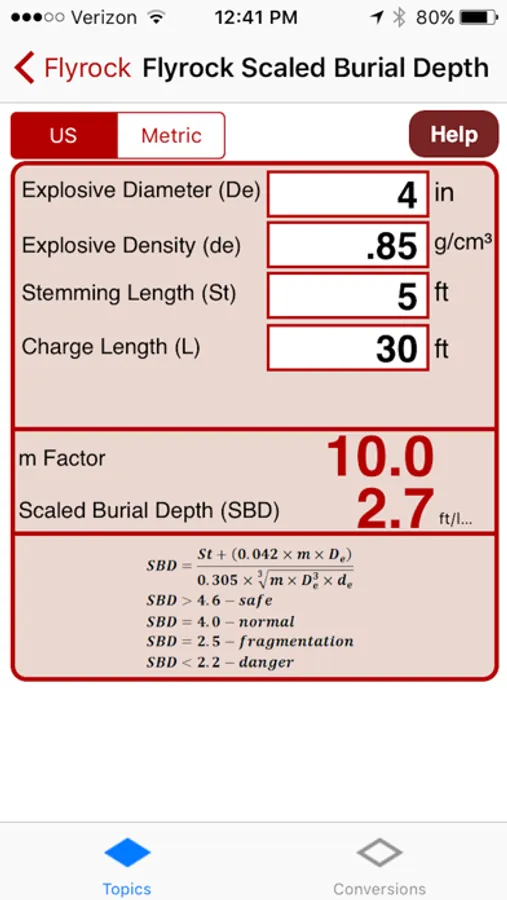
10.5. Scaled Burial Depth
10.6. Stem Length and Collar Flyrock Potential
11. Detonation and Blast-hole pressure
12. Fragmentation Calculations
12.1. Rock Factor
12.2. Uniformity Index
12.3. Important Particle Size
12.4. Convert D50% to Dxx%
12. Weight and Bulk Strength
12.1. Absolute Bulk Strength
12.2. Absolute Weight Strength
12.3. Relative Bulk Strength
12.4. Relative Weight Strength
12.5. Equivalent Weight of Explosive
13. Overpressure Prediction
14. GPS Data Manipulation
14.1. Latitude/Longitude to Distance
14.2. Distance from UTM coordinates
14.3. Distance from State plane coordinates
14.4. Latitude/Longitude to UTM
14.5. UTM to Latitude/Longitude
Supported Conversion Types:
1. Length - meters, kilometers, millimeters, centimeters, micrometers, thou, inches, feet, yard, miles
2. Weight - kilograms, grams, milligrams, tonne, grain, ounces, pounds, ton, imperial ton
3. Velocity - m/s, mm/s, km/s, in/s, ft/s, ft/min, ft/hr, mph, fu/fo
4. Area - m², mm², cm², km², hectare, in², ft², yd², acre, miles²
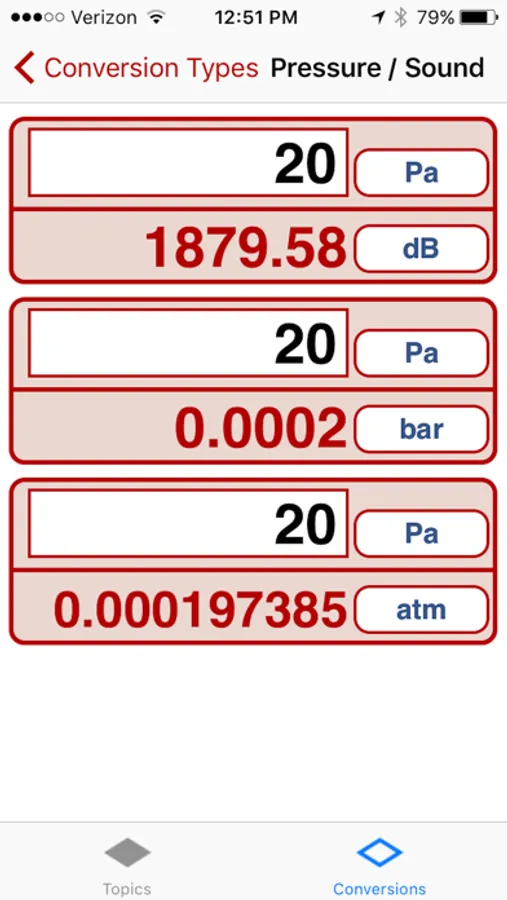
5. Pressure/Sound - Pa, kPa, MPa, GPa, psi, kpsi, bar, kbar, atm, dB
6. Volume - m³, mm³, cm³, liter, in³, ft³, yd³, gal
7. Time - second, millisecond, minute, hour, day, week, month, year
8. Density - kg/m³, t/m³, g/cm³, lb/ft³, lb/yd³, lb/gal, T/yd³, T/ft³
9. Powder Factor - kg/m³, g/m³, lb/yd³, kg/t, g/t, lb/ton, t/g, t/kg, ton/lb
10. Linear Charge Weight - g/m, mg/m, kg/m, grain/ft, lb/ft
11. Energy Density - J/m³, J/cm³, kJ/m³, MJ/m³, cal/ft³, cal/cm³, kcal/ft³, kcal/cm³, Mcal/ft³, Mcal/cm³
12. Specific Energy - J/kg, J/g, kJ/kg, MJ/kg, cal/g, cal/lb, kcal/lb, Mcal/lb, kcal/ton, Mcal/ton
13. Power - watt, kilwatt, horsepower
14. Temperature - celsius, fahrenheit, kelvin
All formulas support metric and imperial systems.
Detailed explanation is provided for each formula.
All entered values are saved for subsequent use and re-use in different formulas.
1. Blast Pattern Design
1.1. Bench Height
1.2. Hole Diameter
1.3. Burden
1.4. Spacing
1.5. Sub-Drill Depth
1.6. Top Stemming
1.7. Deck Stemming
1.8. Base Charge Length
2. Delay Timing
2.1. Hole-to-Hole delays
2.2. Row-to-Row delays
2.3. Avoid supersonic face velocity
2.4. Estimating vibration frequency
2.5. Delay scatter
2.6. Out-of-sequence probability
2.7. Probability of close firing
3. Volume, Weight and Powder Factors
3.1. Volume of Rock per blast hole
3.2. Weight of Rock per blast-hole
3.3. Weight of Explosives per blast-hole
3.4. Loading Density
3.5. Powder Factor
4. Working with Angled Holes
4.1. Hole 'Look-out' distance
4.2. Required hole angle
4.3. Required hole length
4.4. Burden - two angled holes
4.5. Stemming - two angled holes
4.6. Collar distance - two angled holes
5. Pre-split Design
5.1. Pre-split spacing
5.2. Pre-split charge load
5.3. Pre-split stemming height
5.4. Pre-split hole diameter
5.5. Pre-split explosive diameter
6. Decoupled Charges
6.1. Coupling Ratio
6.2. Dropped explosive cartridge diameter
6.3. Decoupled Charge Effective Density
7. Wet Hole Formulas
7.1. No. of Cartridges to clear Water
7.2. Final Height of Water in Wet Hole
8. Abney Levels and Clinometers
8.1. Calculate Bench Height
8.2. Calculate Toe Burden
8.3. Face Angle
9. Scaled Distance and Blast Vibration
9.1. Actual Scaled Distance
9.2. Max Charge Weight
9.3. Minimum Distance
9.4. Predicting Vibration
9.5. Site specific k factor
9.6. Site specific b exponent
9.7. Distance from seismic data
9.8. Acceleration from PPV
9.9. Displacement from PPV
9.10. Explosive Quantity from PPV
9.11. K Factor Converting
9.12. Estimated p-wave velocity
10. Flyrock
10.1. Average Muckpile Displacement
10.2. Extreme Flyrock
10.3. Burden Velocity and Throw
10.4. Burden Based on Throw
10.5. Scaled Burial Depth
10.6. Stem Length and Collar Flyrock Potential
11. Detonation and Blast-hole pressure
12. Fragmentation Calculations
12.1. Rock Factor
12.2. Uniformity Index
12.3. Important Particle Size
12.4. Convert D50% to Dxx%
12. Weight and Bulk Strength
12.1. Absolute Bulk Strength
12.2. Absolute Weight Strength
12.3. Relative Bulk Strength
12.4. Relative Weight Strength
12.5. Equivalent Weight of Explosive
13. Overpressure Prediction
14. GPS Data Manipulation
14.1. Latitude/Longitude to Distance
14.2. Distance from UTM coordinates
14.3. Distance from State plane coordinates
14.4. Latitude/Longitude to UTM
14.5. UTM to Latitude/Longitude
Supported Conversion Types:
1. Length - meters, kilometers, millimeters, centimeters, micrometers, thou, inches, feet, yard, miles
2. Weight - kilograms, grams, milligrams, tonne, grain, ounces, pounds, ton, imperial ton
3. Velocity - m/s, mm/s, km/s, in/s, ft/s, ft/min, ft/hr, mph, fu/fo
4. Area - m², mm², cm², km², hectare, in², ft², yd², acre, miles²
5. Pressure/Sound - Pa, kPa, MPa, GPa, psi, kpsi, bar, kbar, atm, dB
6. Volume - m³, mm³, cm³, liter, in³, ft³, yd³, gal
7. Time - second, millisecond, minute, hour, day, week, month, year
8. Density - kg/m³, t/m³, g/cm³, lb/ft³, lb/yd³, lb/gal, T/yd³, T/ft³
9. Powder Factor - kg/m³, g/m³, lb/yd³, kg/t, g/t, lb/ton, t/g, t/kg, ton/lb
10. Linear Charge Weight - g/m, mg/m, kg/m, grain/ft, lb/ft
11. Energy Density - J/m³, J/cm³, kJ/m³, MJ/m³, cal/ft³, cal/cm³, kcal/ft³, kcal/cm³, Mcal/ft³, Mcal/cm³
12. Specific Energy - J/kg, J/g, kJ/kg, MJ/kg, cal/g, cal/lb, kcal/lb, Mcal/lb, kcal/ton, Mcal/ton
13. Power - watt, kilwatt, horsepower
14. Temperature - celsius, fahrenheit, kelvin
All formulas support metric and imperial systems.
Detailed explanation is provided for each formula.
All entered values are saved for subsequent use and re-use in different formulas.