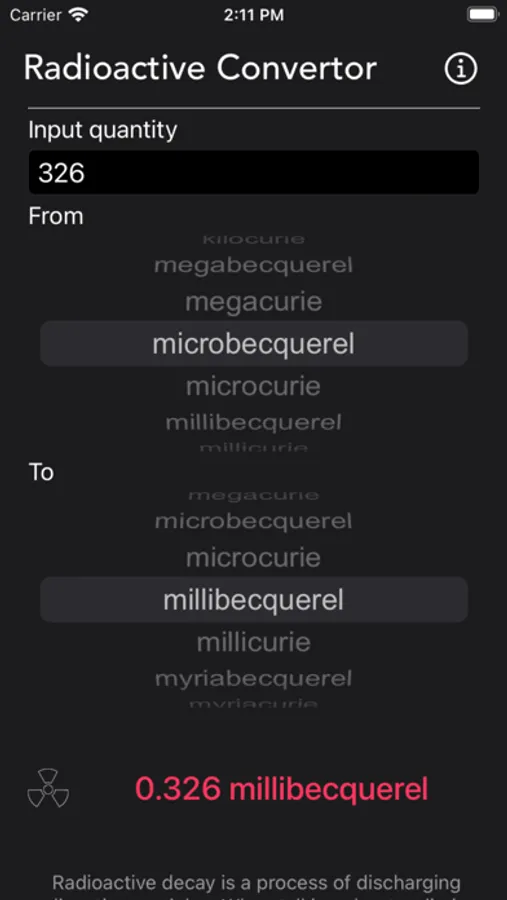
About Radioactivity Conversion
Radioactivity Conversion or Radioactive Decay Unit Conversion - Easily convert between various Radioactive units.
Radioactive decay is the process of emitting radioactive particles, particularly ionizing radiation. Various types of radioactive decay include alpha, beta, and gamma decay, named after the particles emitted during this process. As decay occurs, radioactive particles carry energy away from the nucleus. In some cases, radioactive decay can transform the original nucleus into either a different nucleus or a nucleus in an altered state.
Radioactivity is a property exhibited by certain elements, where the atomic nucleus spontaneously loses electromagnetic energy due to its inherent instability. This phenomenon was first discovered in 1896 by the French physicist Antoine-Henri Becquerel. During this process, ionizing particles and electromagnetic radiation are emitted from the nucleus. Many elements exhibit natural radioactivity.
The duration for radiation to undergo decay varies between elements and their isotopes, often measured in terms of a half-life. The half-life signifies the time it takes for an element's radiation to decrease to half of its initial intensity. Certain elements like uranium and thorium continuously emit radiation and ionizing particles, leading to the formation of different daughter elements while releasing energy in the form of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation.
One particularly significant radioactive element is Radon, a dense, colorless, and odorless gas with a boiling point of -61.8°C (-79.2°F). Radon readily dissolves in water below its boiling point and can freeze at low temperatures.
Thanks for your support and do visit nitrio.com for more apps for your iOS devices.
Radioactive decay is the process of emitting radioactive particles, particularly ionizing radiation. Various types of radioactive decay include alpha, beta, and gamma decay, named after the particles emitted during this process. As decay occurs, radioactive particles carry energy away from the nucleus. In some cases, radioactive decay can transform the original nucleus into either a different nucleus or a nucleus in an altered state.
Radioactivity is a property exhibited by certain elements, where the atomic nucleus spontaneously loses electromagnetic energy due to its inherent instability. This phenomenon was first discovered in 1896 by the French physicist Antoine-Henri Becquerel. During this process, ionizing particles and electromagnetic radiation are emitted from the nucleus. Many elements exhibit natural radioactivity.
The duration for radiation to undergo decay varies between elements and their isotopes, often measured in terms of a half-life. The half-life signifies the time it takes for an element's radiation to decrease to half of its initial intensity. Certain elements like uranium and thorium continuously emit radiation and ionizing particles, leading to the formation of different daughter elements while releasing energy in the form of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation.
One particularly significant radioactive element is Radon, a dense, colorless, and odorless gas with a boiling point of -61.8°C (-79.2°F). Radon readily dissolves in water below its boiling point and can freeze at low temperatures.
Thanks for your support and do visit nitrio.com for more apps for your iOS devices.