About Phoenician Alphabet (Premium)
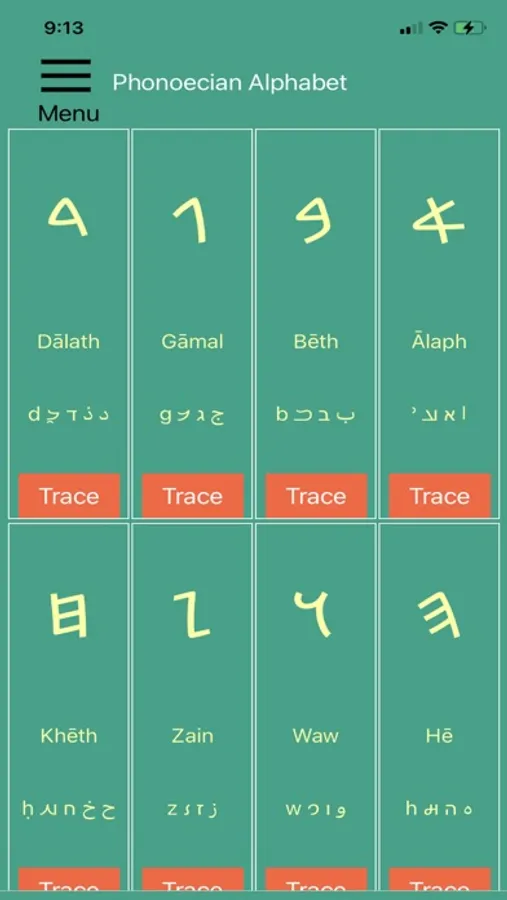
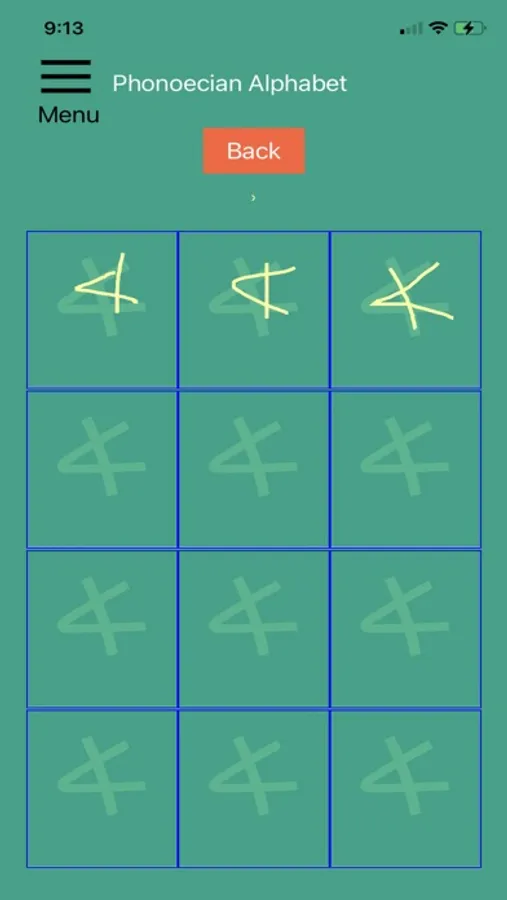
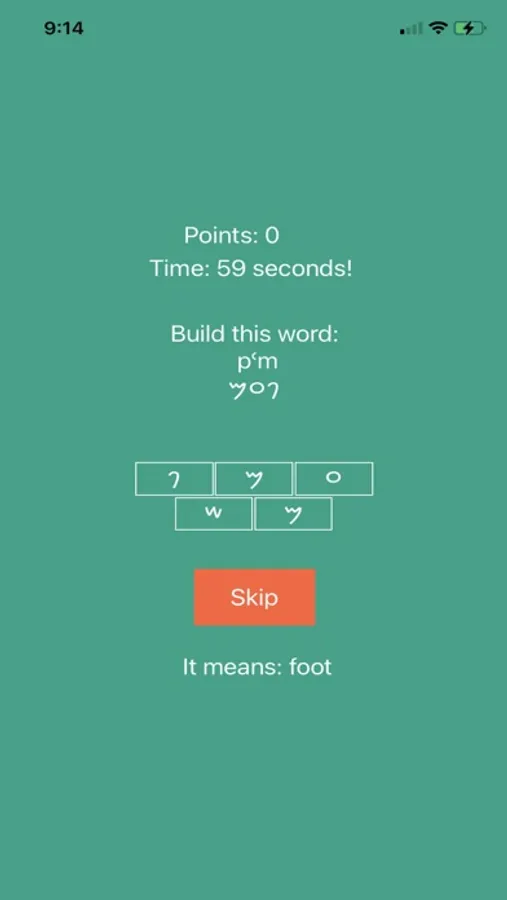
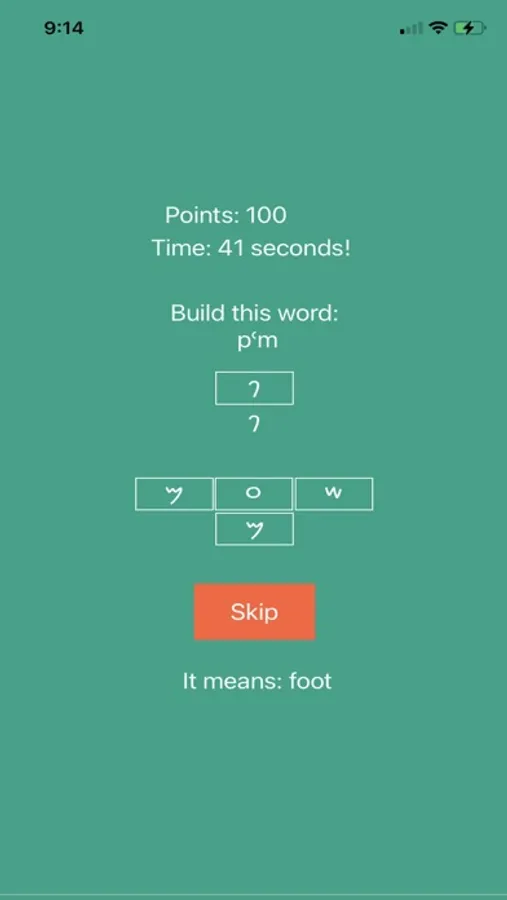
This app can help you get to know the Phonoecian alphabet. Scroll through the letters and study their shapes and sounds. Practice tracing each one until you're familiar-- then quiz yourself on the letters!
Note it is written right-to-left, like most other Semitic writing systems. That is why the first letter is listed on the top right and they go right to left, up to down from Alaph to Taw.
The Phoenician alphabet was used to write the Early Iron Age Canaanite languages, subcategorized by historians as Phoenician, Hebrew, Moabite, Ammonite and Edomite, as well as Old Aramaic. Its use in Phoenicia (coastal Levant) led to its wide dissemination outside of the Canaanite sphere, spread by Phoenician merchants across the Mediterranean world, where it was adopted and modified by many other cultures. It became one of the most widely used writing systems. The Phoenician alphabet proper remained in use in Ancient Carthage until the 2nd century BC (known as the Punic alphabet), while elsewhere it diversified into numerous national alphabets, including the Aramaic and Samaritan, several Anatolian scripts, and the early Greek alphabets. In the Near East, the Aramaic alphabet became especially successful, giving rise to the Jewish square script and Perso-Arabic scripts, among others.
We provide transliteration equivalents for each letter in Latin, Hebrew, Arabic, and Syriac scripts (all of which can be used in the quiz).
Note it is written right-to-left, like most other Semitic writing systems. That is why the first letter is listed on the top right and they go right to left, up to down from Alaph to Taw.
The Phoenician alphabet was used to write the Early Iron Age Canaanite languages, subcategorized by historians as Phoenician, Hebrew, Moabite, Ammonite and Edomite, as well as Old Aramaic. Its use in Phoenicia (coastal Levant) led to its wide dissemination outside of the Canaanite sphere, spread by Phoenician merchants across the Mediterranean world, where it was adopted and modified by many other cultures. It became one of the most widely used writing systems. The Phoenician alphabet proper remained in use in Ancient Carthage until the 2nd century BC (known as the Punic alphabet), while elsewhere it diversified into numerous national alphabets, including the Aramaic and Samaritan, several Anatolian scripts, and the early Greek alphabets. In the Near East, the Aramaic alphabet became especially successful, giving rise to the Jewish square script and Perso-Arabic scripts, among others.
We provide transliteration equivalents for each letter in Latin, Hebrew, Arabic, and Syriac scripts (all of which can be used in the quiz).