About Restrict_Ori
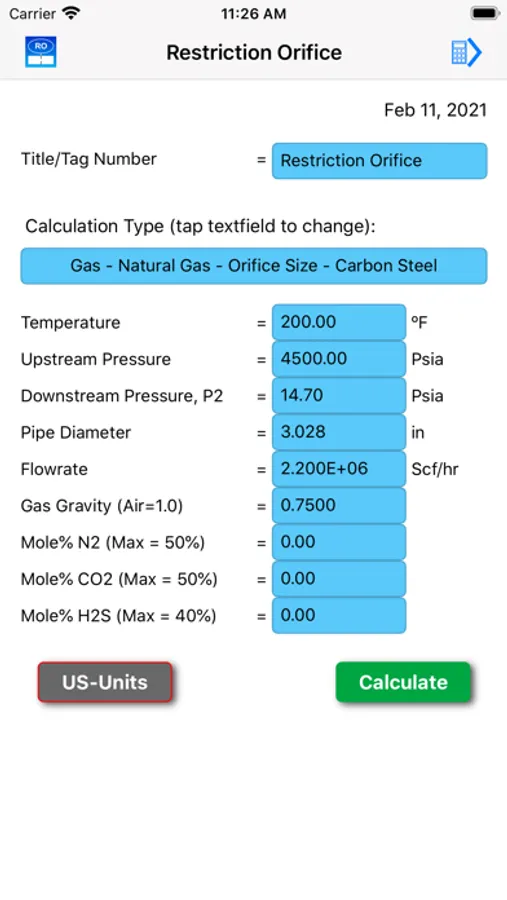
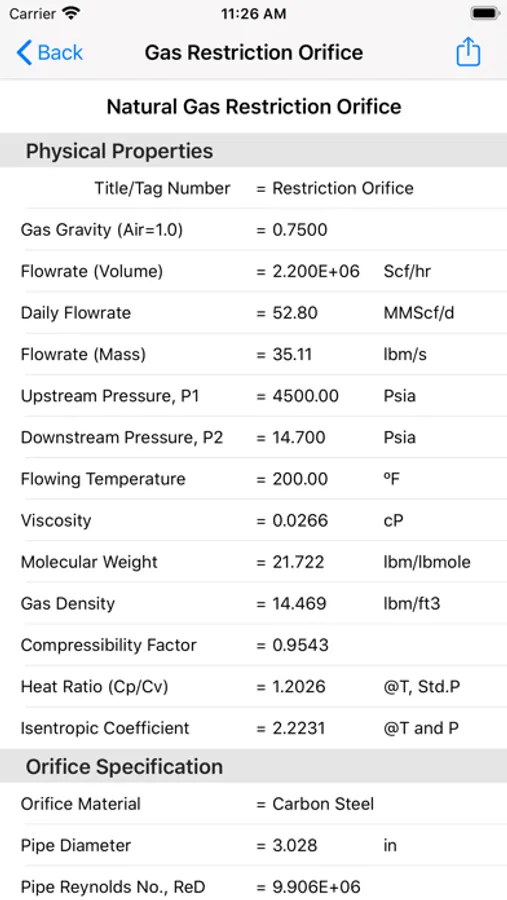
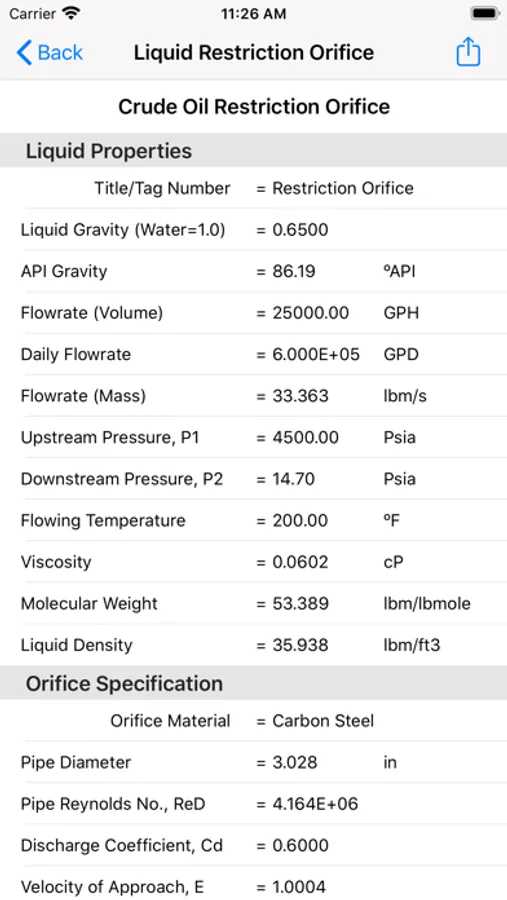
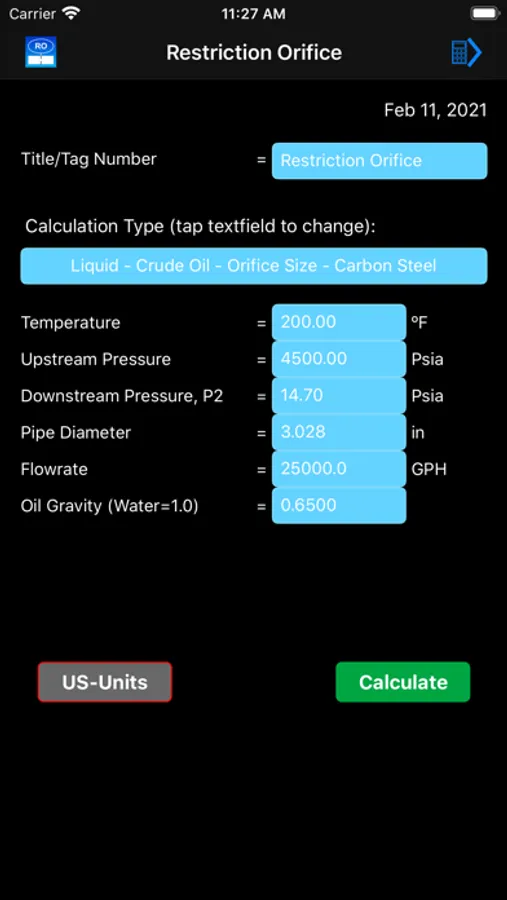
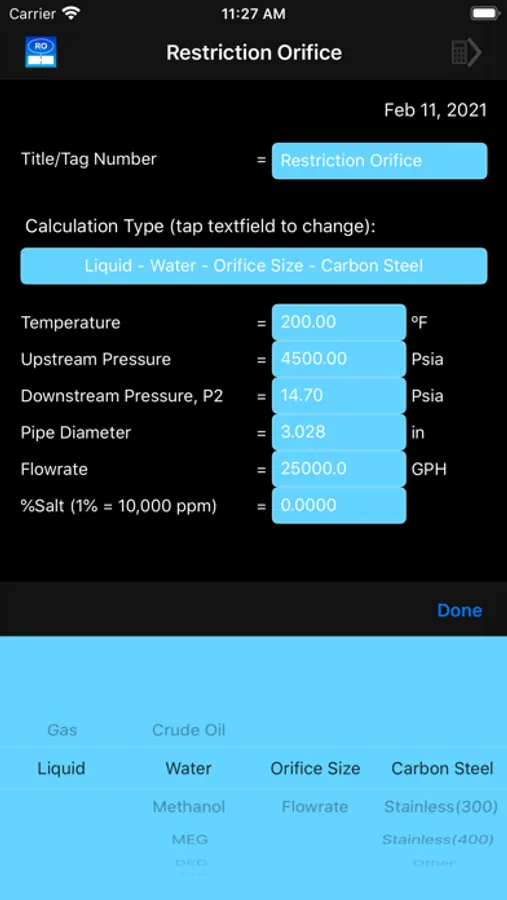
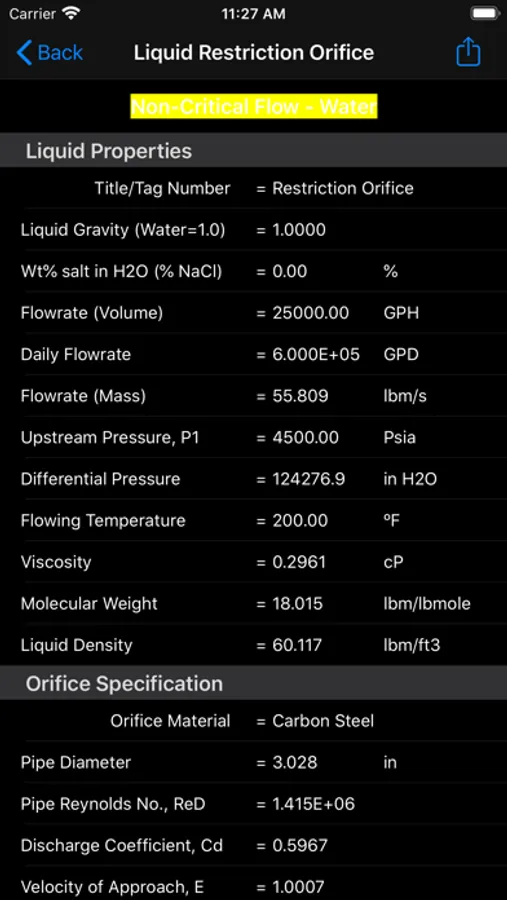
Restrict-Ori calculates gas and liquid restriction orifice sizes and flowrates based on R. W. Miller's "Flow Measurement Engineering Handbook".
For gases this means that sonic velocity (critical flow) exists at the orifice throat, and further decrease in the downstream pressure will not increase the mass flow rate.
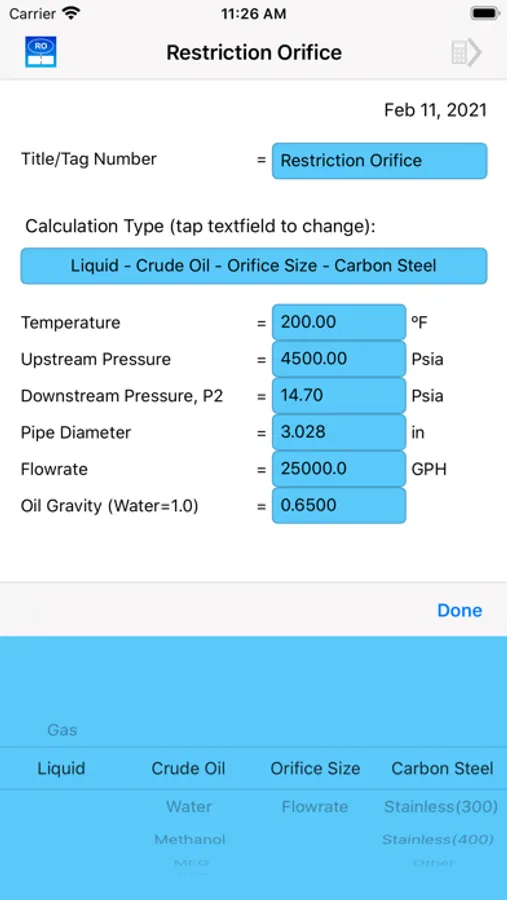
For liquids, choked flow occurs when the orifice decreases the downstream pressure to below the liquid vapor pressure, at that point the liquid will partially flash into bubbles of vapor. If vapor pressure is less than downstream pressure (non-choked flow), the pressure drop is calculated based on empirical equations used for control valves.
For gases this means that sonic velocity (critical flow) exists at the orifice throat, and further decrease in the downstream pressure will not increase the mass flow rate.
For liquids, choked flow occurs when the orifice decreases the downstream pressure to below the liquid vapor pressure, at that point the liquid will partially flash into bubbles of vapor. If vapor pressure is less than downstream pressure (non-choked flow), the pressure drop is calculated based on empirical equations used for control valves.